| |
|
Date : June
7, 2020 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Writer : B.Engr. Koji Makino |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Review : June 10, 2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Calculations for Velocities and Sound Velocities of |
|
|
|
| |
|
Tukuba Meteorite and
Calculations for Temperatures of |
|
|
|
| |
|
the Meteorite by Aerodynamic Heating |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
(When horizontal movement velocity is 1097.4m/s, 747.9m/s was added to
vertical direction |
|
| |
|
velocity to fall to height 13000m above the
ground in lapse of 90 seconds as starting to fall |
|
| |
|
from height of 120km. It rushed to atmosphrere at angle of
15°of east side from the north. |
|
| |
|
The direction shifted to 20°east side by the
power of the earth rotation. The
meteorite falling |
|
| |
|
down route crossed at angle of 35°to the north-south line.
"g" is gravity
acceleration |
|
| |
|
9.8m/s2.) The
meteorite entered atmosphere, and then changed the direction by the
earth |
|
| |
|
rotation. The meteorite started to fall from
altitude of 120km after that. |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
It is a calculating formula which asks for the
temperature of the flight body by which |
|
|
| |
|
aerodynamic heating is done by sound
velocity. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Tah = Rac × r × Tab × Vs2 - 273 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Tah : Aerodynamic Heating Temperature Rac : Air Concentration Ratio r : Form Coefficient |
|
| |
|
Tab : Absolute Temperature Vs : Velocity
of Sound |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Absolute Temperature(Tab)was 273 degree as celsius 0 degree. |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Aerodynamic heating temperature was calculated
on absolute temperature. |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
For it converted to celsius, -273 degree was
added to upper formula. |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
The meteorite was warmed by the solar heat, so
it was not -273℃ really. |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Sound velocity in high altitude is slower
than aboveground, since it changes in each altitudes. |
|
| |
|
All sound velocity are calculated with 330m/s
as average velocity. |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
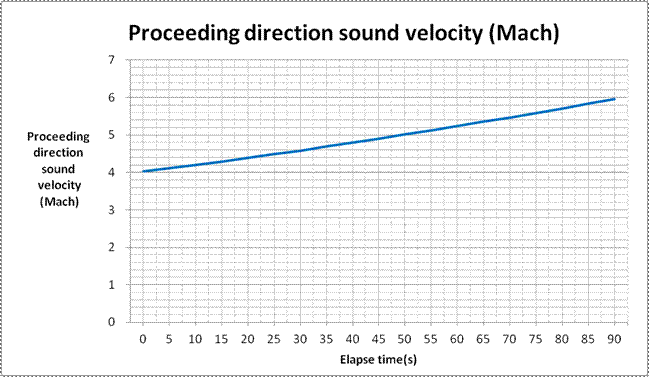
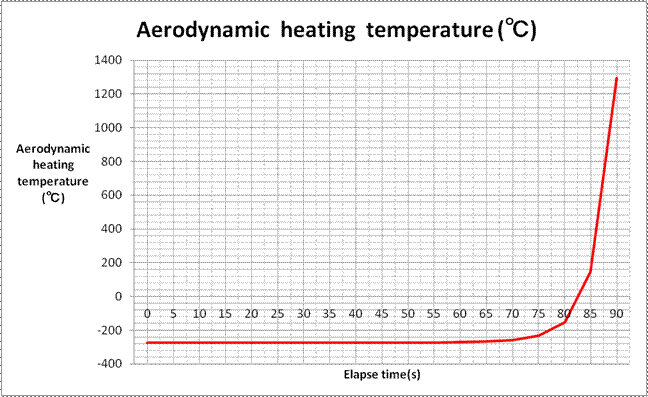
Table 1. calculated proceeding direction sound velocities and
aerodynamic |
|
| |
|
heating
temperatures at elapse time every 5 seconds |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Elapse |
Vertical |
Horizontal |
Proceeding |
Proceeding |
Height a- |
Ratio of air |
Coeffi- |
Aerodyna- |
Visual ob- |
|
| |
time |
direction |
direction |
direction |
direction |
bove ground |
concent- |
cient |
mic heating |
servation |
|
| |
|
velocity |
velocity |
velocity |
sound |
start to fall |
ration to |
of form |
tempe- |
flying |
|
| |
|
V=g×t |
1097.4 |
|
velocity |
from height |
that on |
r = 1 |
rature |
object |
|
| |
|
+747.9 |
|
|
|
120km |
the ground |
|
|
color ・ |
|
| |
(s) |
(m/s) |
(m/s) |
(m/s) |
(Mach) |
(m) |
(%) |
|
(℃) |
state |
|
| |
0 |
747.9
|
1097.4
|
1328.0
|
4.02
|
120000.0
|
0.00
|
1 |
-273.0 |
G., W.C. |
|
| |
5 |
796.9
|
1097.4
|
1356.2
|
4.11
|
116138.0
|
0.00
|
1 |
-273.0 |
G., W.C. |
|
| |
10 |
845.9
|
1097.4
|
1385.6
|
4.20
|
112031.0
|
0.00
|
1 |
-273.0 |
G., W.C. |
|
| |
15 |
894.9
|
1097.4
|
1416.0
|
4.29
|
107679.0
|
0.00
|
1 |
-273.0 |
G., W.C. |
|
| |
20 |
943.9
|
1097.4
|
1447.5
|
4.39
|
103082.0
|
0.00
|
1 |
-273.0 |
G., W.C. |
|
| |
25 |
992.9
|
1097.4
|
1479.9
|
4.48
|
98240.0
|
0.00
|
1 |
-273.0 |
G., W.C. |
|
| |
30 |
1041.9
|
1097.4
|
1513.2
|
4.59
|
93153.0
|
0.00
|
1 |
-273.0 |
G., W.C. |
|
| |
35 |
1090.9
|
1097.4
|
1547.4
|
4.69
|
87821.0
|
0.00
|
1 |
-273.0 |
G., W.C. |
|
| |
40 |
1139.9
|
1097.4
|
1582.3
|
4.79
|
82244.0
|
0.00
|
1 |
-273.0 |
G., W.C. |
|
| |
45 |
1188.9
|
1097.4
|
1618.0
|
4.90
|
76422.0
|
0.00
|
1 |
-273.0 |
G., W.C. |
|
| |
50 |
1237.9
|
1097.4
|
1654.3
|
5.01
|
70355.0
|
0.00
|
1 |
-273.0 |
G., W.C. |
|
| |
55 |
1286.9
|
1097.4
|
1691.3
|
5.13
|
64043.0
|
0.01
|
1 |
-272.3 |
G., W.C. |
|
| |
60 |
1335.9
|
1097.4
|
1728.8
|
5.24
|
57486.0
|
0.03
|
1 |
-270.8 |
G., W.C. |
|
| |
65 |
1384.9
|
1097.4
|
1767.0
|
5.35
|
50684.0
|
0.07
|
1 |
-267.5 |
G., W.C. |
|
| |
70 |
1433.9
|
1097.4
|
1805.6
|
5.47
|
43637.0
|
0.17
|
1 |
-259.1 |
G., W.C. |
|
| |
75 |
1482.9
|
1097.4
|
1844.8
|
5.59
|
36345.0
|
0.46
|
1 |
-233.8 |
G., W.C. |
|
| |
80 |
1531.9
|
1097.4
|
1884.4
|
5.71
|
28808.0
|
1.37
|
1 |
-151.0 |
G., W.C. |
|
| |
85 |
1580.9
|
1097.4
|
1924.5
|
5.83
|
21026.0
|
4.54
|
1 |
148.5 |
G., W.C. |
|
| |
90 |
1629.9
|
1097.4
|
1964.9
|
5.95
|
12999.0
|
16.2
|
1 |
1295.0 |
Bright White |
|
| |
|
G., W.C. : |
Gray, White Cloud |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Date : June
7, 2020 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Writer : B.Engr. Koji Makino |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Review : June 10, 2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
How to calculate about
ratio of air concentration at the altitude to that on the ground |
|
| |
|
Atmospheric pressure at the altitude were
corrected atmospheric pressure at the alititude |
|
| |
|
from data of JMA's Aerological observatory (at
Tukuba) on the very day. |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Ratio of air concentraion were calculated
from atmospheric pressure at the altitude with |
|
| |
|
that on the ground. Atmospheric pressure were data
from the ground to altitude of 33.4km by |
|
| |
|
the observatory. Atmospheric pressure were
calculated by formula of U.S. standard atmosphere, |
|
| |
|
1976. over that altitude. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Date : June 7, 2020 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Writer : B.Engr. Koji Makino |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Review : June 10, 2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
The following table was drawn to confirm
illuminant state every second. |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
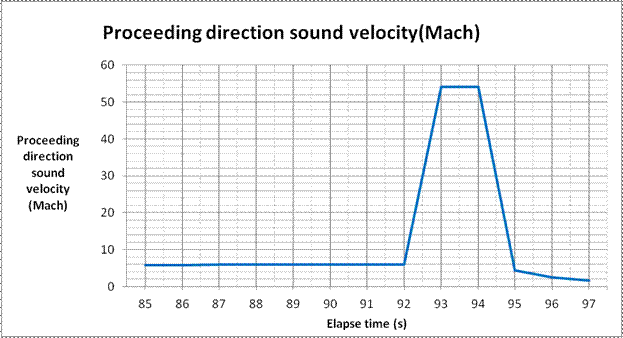
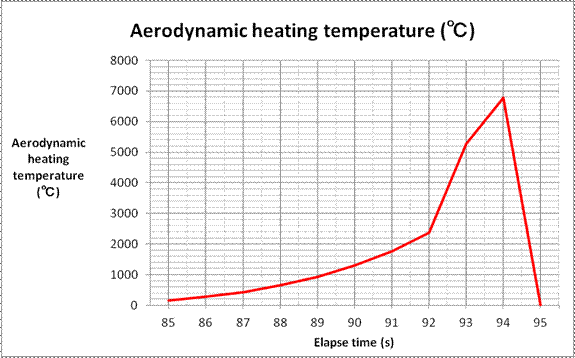
Table 2. calculated proceeding direction sound velocities and
aerodynamic |
|
| |
|
heating
temperatures at elapse time from 85 second to 99 second |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Elapse |
Vertical |
Horizontal |
Proceeding |
Proceeding |
Height a- |
Ratio of air |
Coeffi- |
Aerodyna- |
Visual ob- |
|
| |
time |
direction |
direction |
direction |
direction |
bove ground |
concent- |
cient |
mic heating |
servation |
|
| |
|
velocity |
velocity |
velocity |
sound |
start to fall |
ration to |
of form |
tempe- |
flying |
|
| |
|
V=g×t |
1097.4 |
|
velocity |
from height |
that on |
r = 1 |
rature |
object |
|
| |
|
+747.9 |
|
|
|
120km |
the ground |
|
|
color ・ |
|
| |
(s) |
(m/s) |
(m/s) |
(m/s) |
(Mach) |
(m) |
(%) |
|
(℃) |
state |
|
| |
85 |
1580.9
|
1097.4
|
1924.5
|
5.83
|
21026.0
|
4.54
|
1 |
148.5 |
G., W.C. |
|
| |
86 |
1590.7
|
1097.4
|
1932.5
|
5.86
|
19440.2
|
5.81
|
1 |
270.9 |
G., W.C. |
|
| |
87 |
1600.5
|
1097.4
|
1940.6
|
5.88
|
17844.6
|
7.48
|
1 |
433.2 |
G., W.C. |
|
| |
88 |
1610.3
|
1097.4
|
1948.7
|
5.91
|
16239.2
|
9.68
|
1 |
648.5 |
Light Pink |
|
| |
89 |
1620.1
|
1097.4
|
1956.8
|
5.93
|
14624.0
|
12.6
|
1 |
931.7 |
Orenge |
|
| |
90 |
1629.9
|
1097.4
|
1964.9
|
5.95
|
12999.0
|
16.2
|
1 |
1295.0 |
Bright White |
|
| |
91 |
1639.7
|
1097.4
|
1973.0
|
5.98
|
11364.2
|
20.9
|
1 |
1761.8 |
Big Flash |
|
| |
92 |
1649.5
|
1097.4
|
1981.2
|
6.00
|
9719.6
|
26.9
|
1 |
2374.9 |
Huge Flash |
|
| |
93 |
1659.3
|
17800.0
|
17877.2
|
54.17
|
8065.2
|
34.6
|
0.02
|
5269.6 |
Y.W.P. |
|
| |
94 |
1669.1
|
17800.0
|
17878.1
|
54.18
|
6401.0
|
44.0
|
0.02
|
6776.5 |
Y.W.P. |
|
| |
95 |
800.0
|
1200.0
|
1442.2
|
4.37
|
5601.0
|
49.3
|
−− |
−−− |
P.B. |
|
| |
96 |
600.0
|
600.0
|
848.5
|
2.57
|
5001.0
|
53.4
|
−− |
−−− |
M.S.D. |
|
| |
97 |
400.0
|
400.0
|
565.7
|
1.71
|
4601.0
|
56.3
|
−− |
−−− |
E.A.M.S.D. |
|
| |
98 |
300.0
|
300.0
|
424.3
|
1.29
|
4301.0
|
58.6
|
−− |
−−− |
H.T.M.S. |
|
| |
99 |
150.0
|
200.0
|
250.0
|
0.76
|
4151.0
|
59.8
|
−− |
−−− |
H.T.M.S. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
These velocitys are calculated |
G., W.C. : |
Gray, White Cloud |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
to divide moving distance in |
Y.W.P.
: |
Yellow White Photosphere |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
2 seconds by time. |
|
P.B. : |
Photosphere Burst |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
Those velocitys are put to |
M.S.D.
: |
Molten Substance Diffussion |
|
|
| |
|
|
suitable value. |
|
E.A.M.S.D.: |
Explosion After Molten Substance Diffusion |
|
| |
|
|
Calculated height by observed |
H.T.M.S. : |
High Temperature Meteorites Shower |
|
| |
|
|
elevation angle at sighting site. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
When it became a photosphere, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
since it became the sphere fully, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
that form factor becomes small. |
|
|
|
June 10, 2023 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
How to determine the
coefficient of form |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
The shape of flying object gives influence for
aerodynamic heating. It is
determined |
|
|
| |
|
aerodynamic heating coefficient of form r = 1 through trial and error because
meteorite is |
|
| |
|
almost sphere. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
The molten substance
continued to spread after photosphere bursting. So the yellow |
|
| |
|
white photosphere became early for 1second.
Ratios of air concentration to that on the |
|
| |
|
ground were reviewed, those numerical values
were revised. |
|
August 2, 2021 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
When lapse time were from
90 second to 92 second, it became the huge flash fireball |
|
| |
|
and the velocity became 1.98km/s (Mach 6.0). The
ice of the meteorite vapored in large |
|
| |
|
amounts, it became a huge black cloud. When
lapse time were from 93 second to 94 second, |
|
| |
|
it became a photosphere and it flew with the
velocity 17.9km/s
(Mach 54.2). |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
August 2, 2021 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Date : June 7, 2020 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Writer : B.Engr. Koji Makino |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Review : June 10, 2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
The confirmation with the
actual temperature has not been performed about |
|
|
|
| |
|
calculative numerical values with aerodynamic
heating temperatures from 93 second |
|
|
| |
|
to 94 second at the lapse time. Till 92
second, it is confirmed from the relation |
|
|
|
| |
|
between luminescent color and temperature
above the ground. |
|
August 2, 2021 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
When the temperature
inside a photosphere exceeds 2862 ℃, the ferrum of an |
|
|
| |
|
interiority substance becomes gas and it will
vapor. Since the interiority substance of |
|
|
| |
|
the photosphere turned into a molten
substance and the waterish viscosity was shown, |
|
| |
|
it was surmised that the bulk temperature of a
photosphere was probably 2200 ℃. |
|
|
| |
|
Supposing the form factor was 1, since the
temperature would be too high, it set the |
|
|
| |
|
form factor to 0.02. Probably, the surface
temperature of a photosphere will be |
|
|
|
| |
|
from 5000℃ to 7000℃. |
|
|
|
|
June 10, 2023 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Date : June
7, 2020 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Writer : B.Engr. Koji Makino |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Review : June 10, 2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
the Verification about the
Altitude of 120km where |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
the Meteorite Start to Fall from. |
|
|
| |
|
(It is verified by comparing calculated
distances with measured distances |
|
|
|
| |
|
on route map at each illuminant state whether it is suitable that the
height of meteorite |
|
| |
|
start to fall from 120km. ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Table 1 : Table of doing decision that
caluculated horizontal distances compare with |
|
| |
|
measured distances on the route map at each illuminant state from
point of |
|
| |
|
meteorite starting to fall |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Calculation
of the horizontal distance from point of |
Verification |
|
|
| |
|
starting
meteorite fall, the height and the illuminant state |
(Measurement on the route map) |
|
|
| |
|
Elapsed |
Horizontal |
Distance |
Height |
Calculat- |
Route map |
Route map |
Deci- |
|
|
| |
|
time from |
direction |
from |
|
ed temp. |
point name |
measure. |
sion |
|
|
| |
|
starting p. |
velocity |
starting p. |
|
illuminant |
|
distance |
(within 2% |
|
|
| |
|
(s) |
(m/s) |
(m) |
(m) |
state |
|
(mm) |
of error) |
|
|
| |
|
88 |
1097.4 |
96571
|
16239.2 |
Light Pink |
Lumi. Start |
96.5 |
Agree. |
|
|
| |
|
89 |
1097.4 |
97669
|
14624.0 |
Orenge |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
90 |
1097.4 |
98766
|
12999.0
|
Bright White |
Bright White |
98.5 |
Agree. |
|
|
| |
|
91 |
1097.4 |
99863
|
11364.2
|
Big Flash |
---- |
---- |
---- |
|
|
| |
|
92 |
1097.4 |
100961
|
9719.6
|
Huge Flash |
Huge Flash |
102 |
Agree. |
|
|
| |
|
93 |
17800 |
118761
|
8065.2
|
Y.W.Photo. |
---- |
---- |
---- |
|
|
| |
|
94 |
17800 |
136561
|
6401.0
|
Y.W.Photo. |
---- |
---- |
---- |
|
|
| |
|
95 |
1200 |
137761
|
5601.0
|
P.B. |
---- |
---- |
---- |
|
|
| |
|
96 |
600 |
138361
|
5001.0
|
M.S.D. |
M.S.D. |
138 |
Agree. |
|
|
| |
|
97 |
400 |
138761
|
4601.0
|
E.A.M.S.D. |
---- |
---- |
---- |
|
|
| |
|
98 |
300 |
139061
|
4301.0
|
H.T.M.S. |
---- |
---- |
---- |
|
|
| |
|
99 |
200 |
139261
|
4151.0
|
H.T.M.S. |
---- |
---- |
---- |
|
|
| |
|
The route map is scale 1/1000000. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
1mm on the route map correspond to 1km in real
distance value. |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
starting p. : starting point of meteorite fall |
Lumi. Start : Luminous Start |
|
|
| |
|
Y.W.Photo. : Yellow White Photosphere |
P.B.
: Photosphere Burst |
|
| |
|
M.S.D. : Molten
Substance Diffusion |
Agree. :
Agreement |
|
|
|
| |
|
E.A.M.S.D. :
Explosion After Molten Substance Diffusion |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
H.T.M.S. : High Temperature Meteorites
Shower |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Agreement means that calculated distance is
equal with measured distance on the route map. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
Comparation with calculated horizontal
distance and measured distance from |
|
| |
|
|
starting point of merteorite fall |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
This numeric value match up with
calculated height from witnessed elevation angle. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
The molten substance continued to spread after
photosphere bursting. |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
So the yellow white photosphere became early
for 1second and the molten substance diffusion |
|
| |
|
time was added on the table 1. |
|
|
|
August 2, 2021 |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
※ In the case of falling from height of
120km, the calculated value of
the distance |
|
|
| |
|
were suitable well
with the measured distance on the route map at each illuminant |
|
|
| |
|
state point from the
starting point. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
It is judged that the meteorite starting to |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
fall from height of 120km is suitable. |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Transl. date : |
August 28, 2020 |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Translator
: |
B.Engr.
Koji Makino |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Transl. rev.
: |
June 12, 2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|